Cisco IOS Switches
Cisco IOS switches are traditional Cisco Catalyst switches running the classic IOS operating system. These switches are widely deployed in enterprise environments and provide robust Layer 2/3 switching capabilities with comprehensive management features.
Supported Models
| Model/Series | Notes |
|---|---|
| Catalyst 2960 Series | Layer 2 access switches |
| Catalyst 3560 Series | Layer 2/3 access switches |
| Catalyst 3750 Series | Stackable Layer 2/3 switches |
| Catalyst 3850 Series | Stackable access/distribution switches |
| Other IOS-based switches | Generally supported if running classic IOS |
Note: For Catalyst switches running IOS-XE (such as Catalyst 9000 series), see the Cisco Catalyst IOS-XE documentation.
Features Supported
| Feature | Supported | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Config Sync | Yes | Automatic configuration synchronization from rXg |
| Auto Bootstrap | Yes | Zero-touch onboarding from factory-default state via DHCP discovery |
| SNMP Monitoring | Yes | CPU, memory, and port statistics collection |
| LLDP Neighbor Discovery | Yes | Automatic detection of connected devices |
| Switch Port Import | Yes | Automatic import and management of switch ports |
| 802.1X Authentication | Yes | Port-based network access control |
| MAC Authentication Bypass (MAB) | Yes | MAC-based authentication for non-802.1X devices |
| Dynamic VLAN Assignment | Yes | RADIUS-assigned VLAN based on authentication |
| DHCP Snooping | Yes | Protection against rogue DHCP servers |
| Firmware Management | No | Manual firmware upgrades required |
| SPB-m Fabric | No | Not supported on classic IOS |
Prerequisites
Firmware Requirements
- IOS 15.x or later recommended for full feature support
- SSHv2 support required (IOS 12.1(19)EA1 or later)
Network Requirements
- Management IP connectivity to rXg
- SSH access (TCP port 22)
- SNMP access (UDP port 161)
- RADIUS connectivity (UDP ports 1812, 1813)
Onboarding Process
Automatic Onboarding
Cisco IOS switches can be automatically onboarded from a factory-default state when:
- The switch is connected to the network and obtains a DHCP address from rXg
- A switch record exists in rXg with the switch's MAC address configured
- Valid SSH credentials are provided that match the switch's default or pre-configured credentials
The auto-bootstrap process will: - Configure the management VLAN and static IP address - Set up SSH access and credentials - Configure SNMP community string - Apply basic AAA and RADIUS configuration - Configure the uplink port as a trunk
Manual Onboarding
For manual configuration, apply the bootstrap commands below via console or existing network access.
Bootstrap Commands
The following baseline configuration changes are required to bring a Cisco IOS switch into a state compatible with rXg config sync.
Disable Unnecessary Services
Disable TCP and UDP small servers that run in the switch for diagnostics purposes:
no service udp-small-servers
no service tcp-small-servers
Disable local HTTP server (not used with config sync):
no ip http server
Enable password encryption service:
service password-encryption
Enable SSH Access
Enable SSHv2, generate the necessary RSA key, and enable SSH as the preferred transport protocol on the VTY lines. Note that the IP domain name must also be set for the RSA key to be generated.
ip domain name <your-local-domain-name>
crypto key generate rsa general-keys modulus 4096
ip ssh version 2
line vty 0 15
login local
transport input ssh
exit
Configure Credentials
Configure the 'enable' and admin passwords:
enable secret <secret-enable-password>
username <username> secret <password>
Ensure the corresponding credentials are configured in the rXg 'Network::Wired::Switches' scaffold:
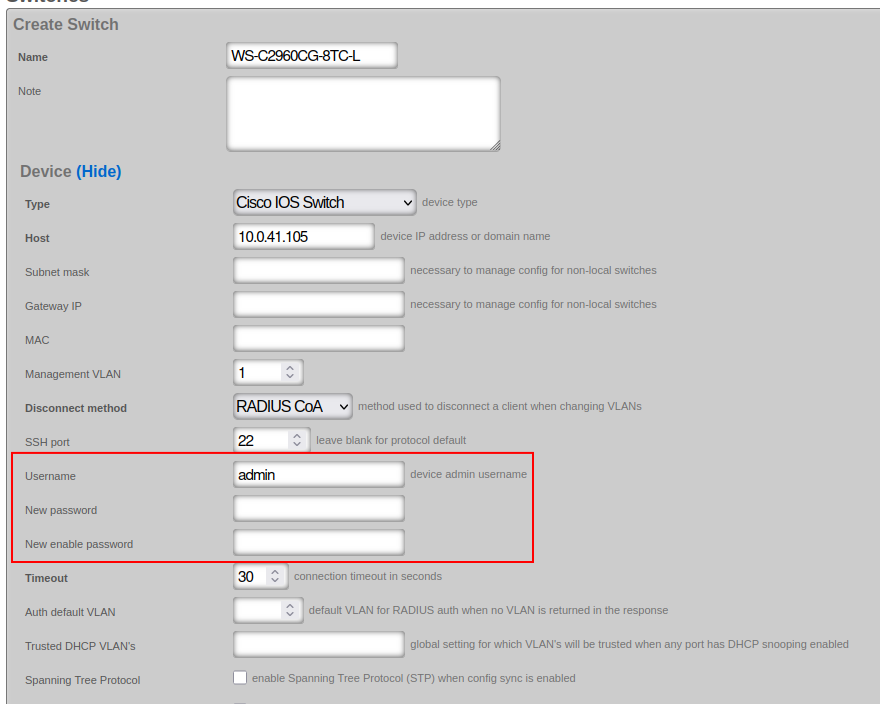
Configuration
SNMP Configuration
The SNMP read-only community access needs to be configured:
snmp-server community public ro
The default community used by rXg ('public') can be modified in the Cisco IOS switch configuration under 'Network::Wired::Switches' scaffold, in the 'Network Monitor' section. The example shows a non-default community name of 'publick':
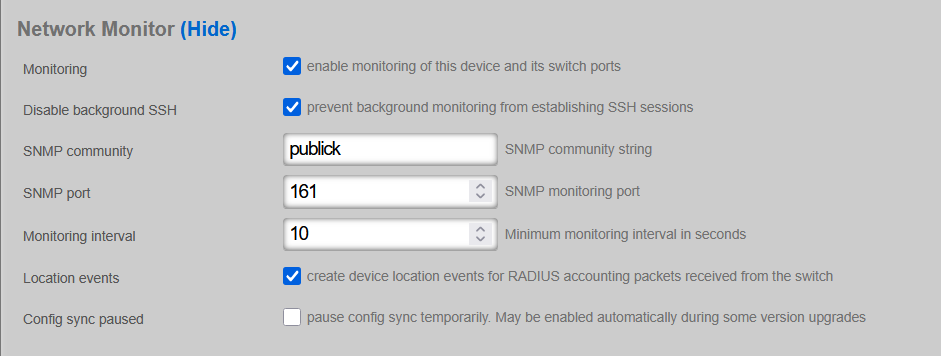
In active production networks, the use of non-default SNMP communities is strongly recommended.
VTP VLAN Mode
If the Cisco IOS switch supports VTP, change the VTP mode from the default 'client' to 'transparent':
(config)#vtp mode transparent
Once modified, verify the status:
show vtp status
VTP Version capable : 1 to 3
VTP version running : 3
VTP Domain Name : NAME
VTP Pruning Mode : Disabled
VTP Traps Generation : Disabled
Device ID : d4ad.7139.5480
Feature VLAN:
--------------
VTP Operating Mode : Transparent
Number of existing VLANs : 5
Number of existing extended VLANs : 0
Maximum VLANs supported locally : 1005
Feature MST:
--------------
VTP Operating Mode : Transparent
RADIUS / AAA Configuration
RADIUS Server Setup
Create a RADIUS server configuration on the switch. The IP address (radius-server-ip) must be reachable from the switch management interface (typically the default gateway). The RADIUS server key (radius-server-key) is obtained from the 'Services::RADIUS::RADIUS Server Options' scaffold:
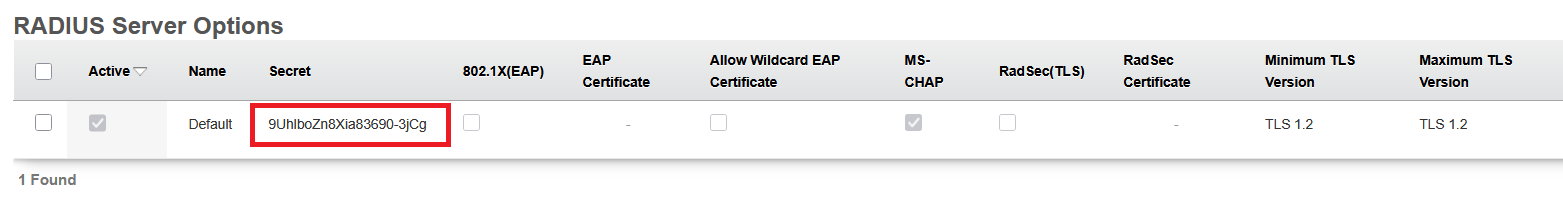
radius server rXg
address ipv4 <radius-server-ip> auth-port 1812 acct-port 1813
key <radius-server-key>
exit
Basic AAA Configuration
Configure AAA settings for config sync with rXg:
aaa new-model
aaa authentication dot1x default group radius
dot1x system-auth-control
identity profile default
MAB with Dynamic VLAN Assignment
MAC Authentication Bypass (MAB) with Dynamic VLAN Assignment provides network access control for devices that do not support 802.1X (IP phones, printers, cameras, IoT devices), placing them into the correct VLAN based on their MAC address.
The switch learns the MAC address and sends it as both username and password to the RADIUS server. Upon successful authentication, the RADIUS server returns VLAN assignment attributes:
- Tunnel-Type = VLAN (Attribute 64)
- Tunnel-Medium-Type = 802 (Attribute 65)
- Tunnel-Private-Group-ID = VLAN ID (Attribute 81)
System-Level Configuration:
Variables used:
- radius-server-ip: IP address of the RADIUS server
- radius-server-key: Authentication key of the RADIUS server
- radius-server-name: Arbitrary name for the RADIUS server (e.g., 'rXg')
aaa new-model
!
# Defines authentication method for 802.1X (also used by MAB fallback)
aaa authentication dot1x default group radius
# Defines authorization method for network access
aaa authorization network default group radius
# Defines accounting for 802.1X sessions
aaa accounting dot1x default start-stop group radius
# Enable dynamic authorization (CoA - Change of Authorization)
# This allows the RADIUS server to dynamically re-authenticate or change VLANs without user re-authentication.
aaa server radius dynamic-author client <radius-server-ip> server-key 0 <radius-server-key>
# use the same session ID for all AAA accounting service types within a single call
aaa session-id common
# Define the RADIUS server(s)
radius server <radius-server-name>
address ipv4 <radius-server-ip> auth-port 1812 acct-port 1813
key 0 <radius-server-key>
# Send vendor-specific attributes (critical for dynamic VLAN assignment)
radius-server vsa send authentication
radius-server vsa send accounting
# Enable 802.1X globally (MAB requires this)
dot1x system-auth-control
Interface-Level Configuration:
The onboarding-vlan-id is the fallback VLAN used when no VLAN is assigned by the RADIUS server.
# MAB / dot1x authentication commands
authentication event fail action next-method
authentication host-mode multi-auth
authentication order mab dot1x
authentication periodic
authentication timer inactivity server
mab
# STP port protect commands
spanning-tree bpduguard enable
spanning-tree bpdufilter enable
spanning-tree guard root
spanning-tree guard loop
udld port aggressive
# fall back (onboarding) VLAN
switchport mode access
switchport access vlan <onboarding-vlan-id>
Monitoring Capabilities
| Metric | Collection Method | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| CPU Usage | SNMP | Collected at configured monitoring interval |
| Memory Usage | SNMP | Collected at configured monitoring interval |
| Port Statistics | SNMP | Packets in/out, errors, discards |
| Port Status | SNMP | Up/down, speed, duplex |
| LLDP Neighbors | SNMP | Connected device discovery |
Troubleshooting
Common Issues
Issue: Switch shows offline in rXg
Symptom: Switch appears offline despite being reachable via ping Cause: SSH or SNMP connectivity issues Resolution: Verify SSH credentials, SNMP community string, and firewall rules
Issue: Config sync fails
Symptom: Configuration changes not being applied to switch Cause: VTP mode not set to transparent, or credential mismatch Resolution: Verify VTP mode is 'transparent' and credentials match rXg configuration
Issue: Dynamic VLAN not assigned
Symptom: Devices remain in onboarding VLAN after authentication
Cause: RADIUS server not returning VLAN attributes, or VSA not enabled
Resolution: Verify radius-server vsa send authentication is configured
Diagnostic Commands
show vtp status
show aaa servers
show dot1x all
show authentication sessions
show radius statistics
show snmp
Known Limitations
- SPB-m fabric not supported (use Extreme VSP/ERS for fabric deployments)
- Firmware management not automated; upgrades must be performed manually
- Some older IOS versions may have limited SSHv2 support
Operational Caveats
- VTP must be set to 'transparent' mode for proper VLAN management
- RSA key generation is required before SSH will function
- Non-default SNMP communities are strongly recommended in production
- The 'admin' username can be customized but must match between switch and rXg