Health Notices System
The rXg incorporates a sophisticated health monitoring and notification system that continuously monitors all critical aspects of system operation, network infrastructure, and service delivery. Health notices serve as the primary mechanism for alerting administrators to conditions that require attention, from routine capacity warnings to critical system failures.
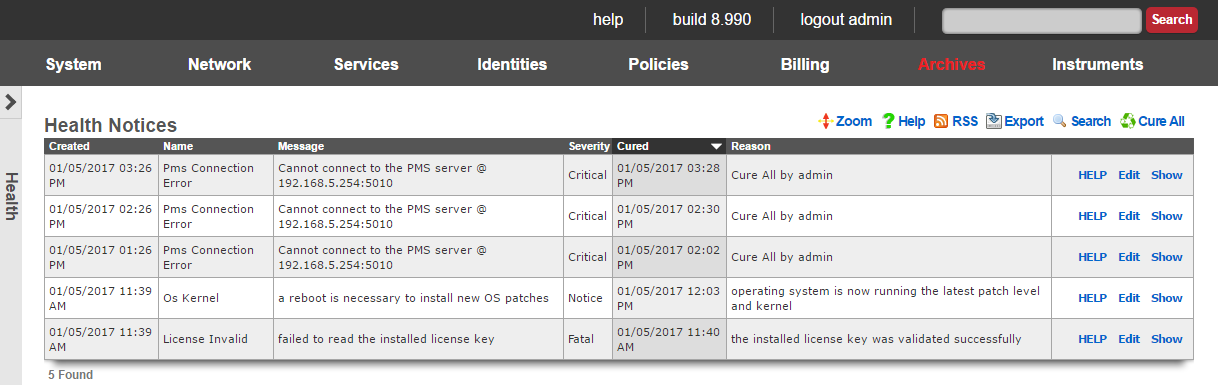
The health notices system operates as both a proactive monitoring tool and a reactive alerting mechanism. It continuously evaluates system metrics against predefined thresholds and generates notices when conditions warrant administrative attention. For clustered deployments, individual rXg nodes report all health notices to the cluster controller for centralized logging and management, providing administrators with a unified view of the entire infrastructure's health status.
Health Notice Lifecycle and Mechanism
Health notices follow a well-defined lifecycle that begins with detection and progresses through notification, acknowledgment, and resolution phases. The system creates health notices through multiple detection mechanisms including real-time monitoring, scheduled checks, exception handling, and external system integration.
When a monitored condition exceeds its threshold or an error condition occurs, the system immediately creates a health notice record containing comprehensive details about the condition, including a unique identifier, severity level, timestamp, descriptive messages, and contextual information. The notice generation process is atomic, ensuring that critical conditions are never lost due to system race conditions or failures.
The system maintains both short and long message formats for each health notice. The short message provides a concise summary suitable for dashboard displays and quick reference, while the long message contains detailed diagnostic information, stack traces, configuration details, and remediation guidance. This dual-message approach ensures that administrators can quickly assess situations while having access to comprehensive diagnostic data when needed.
Health Notice Severity Levels
The rXg health notice system employs four distinct severity levels, each corresponding to different urgency levels and required response timeframes.
NOTICE level health notices indicate informational conditions that administrators should be aware of but do not require immediate action. These typically include successful completion of maintenance operations, configuration changes that completed successfully but may have implications for future operations, or approaching but not critical threshold conditions. Notice-level health notices serve primarily as audit trails and early indicators of trends that may require future attention.
WARNING level health notices indicate conditions that require administrative attention within a reasonable timeframe but do not immediately threaten system operation. These include capacity utilization approaching configured thresholds, configuration inconsistencies that may impact performance, deprecated feature usage, non-critical service disruptions, and environmental conditions approaching operational limits. Warning-level notices often represent opportunities for proactive intervention before conditions escalate to critical levels.
CRITICAL level health notices indicate serious conditions that require immediate administrative attention and may impact system operation if not addressed promptly. These include service failures, significant capacity constraints, authentication system problems, network connectivity issues affecting core functionality, and hardware conditions that may lead to failure. Critical-level notices typically indicate that some system functionality may already be compromised or is at immediate risk of compromise.
FATAL level health notices represent the most severe conditions that require immediate emergency response. These indicate system conditions that have already caused significant service disruption or present imminent risk of complete system failure. Fatal-level notices include core system component failures, complete network isolation, licensing violations that prevent operation, and hardware failures that compromise system integrity.
Health Notice Creation and Sources
Health notices originate from multiple sources throughout the rXg system, each contributing specialized monitoring capabilities for different aspects of system operation. The backend monitoring subsystem continuously evaluates system resources, network connectivity, service health, and infrastructure status. This subsystem generates notices for conditions such as memory utilization, filesystem capacity, network interface status, and process health.
The web portal subsystem creates health notices when exceptions occur during user interactions, asset compilation failures prevent proper portal operation, or authentication system irregularities are detected. These notices help administrators identify and resolve issues that directly impact end-user experience and system accessibility.
The DHCP monitoring subsystem generates notices related to IP address pool utilization, lease conflicts, configuration errors, and service availability. Given the critical role of DHCP in network operations, these notices help prevent IP address exhaustion and ensure continuous network connectivity for end users.
Database and transaction monitoring creates notices when connection failures occur, transaction deadlocks are detected, or data integrity issues arise. These notices help maintain system reliability and data consistency across all rXg operations.
Network infrastructure monitoring generates notices for ping target failures, uplink status changes, access point connectivity issues, and general network reachability problems. This monitoring extends beyond the rXg itself to include critical network infrastructure components that affect overall service delivery.
Automatic Health Notice Curing
The rXg health notice system includes sophisticated automatic curing capabilities that resolve health notices when the underlying conditions improve without administrative intervention. This auto-curing mechanism prevents the accumulation of outdated notices and ensures that the health notice dashboard accurately reflects current system status.
Auto-curing operates through continuous re-evaluation of monitored conditions. When a health notice exists for a particular condition, the monitoring system continues to evaluate that condition at regular intervals. If the condition returns to acceptable parameters and remains stable for a configured period, the system automatically marks the health notice as cured and records the resolution details.
For capacity-related health notices, auto-curing occurs when utilization drops below the warning threshold and remains stable. For connectivity-related notices, auto-curing happens when network reachability is restored and sustained. For service-related notices, auto-curing takes place when the affected services return to normal operation and pass health checks.
The auto-curing process includes comprehensive logging of resolution details, including timestamps, final condition values, and the duration between the original notice creation and automatic resolution. This information helps administrators understand the natural lifecycle of system conditions and identify patterns that may warrant proactive intervention.
Certain types of health notices require manual intervention and cannot be automatically cured. These include configuration errors that require administrative correction, hardware failures that need physical intervention, licensing issues that require administrative action, and security-related notices that require explicit administrator acknowledgment.
Manual Health Notice Curing
Administrators can manually cure health notices through the web interface when conditions require explicit acknowledgment or when automatic curing is inappropriate for the situation. Manual curing allows administrators to add specific resolution notes, document corrective actions taken, and ensure that critical conditions receive proper attention before being marked as resolved.
The manual curing process requires administrators to provide both short and long resolution messages. The short message provides a brief description of the resolution action, while the long message allows for detailed documentation of troubleshooting steps, corrective measures taken, root cause analysis, and preventive actions implemented.
Manual curing also supports bulk operations, allowing administrators to cure multiple related health notices simultaneously when addressing systemic issues or completing maintenance activities that resolve multiple conditions. This bulk capability streamlines administrative workflows while maintaining proper audit trails for all resolution activities.
Custom Threshold Configuration
The rXg health notice system provides extensive customization capabilities for threshold values and monitoring parameters, allowing administrators to tailor the monitoring sensitivity to their specific operational requirements and environment characteristics. Threshold configuration is distributed across multiple system areas, each corresponding to different categories of monitored conditions.
Capacity monitoring thresholds can be configured for filesystem utilization, memory usage, DHCP pool utilization, license limits, connection states, and various other resource pools. Administrators can typically set both warning and critical threshold levels, allowing for graduated response to approaching capacity limits. These thresholds are expressed as percentages of maximum capacity, absolute values, or rate-based limits depending on the specific resource type.
Network monitoring thresholds include ping timeout values, retry counts, failure duration tolerances, and connectivity test intervals. These settings allow administrators to balance monitoring sensitivity with network conditions, accommodating temporary connectivity issues while ensuring prompt detection of sustained problems.
Performance monitoring thresholds encompass load average limits, response time tolerances, queue depth limits, and throughput baselines. These thresholds help identify performance degradation before it significantly impacts user experience.
Service-specific thresholds are available for individual system components, including database connection timeouts, web server response limits, authentication service tolerances, and external system integration parameters. These specialized thresholds ensure that service-specific conditions are monitored according to their unique operational characteristics.
Comprehensive Health Notice Types
The rXg system supports an extensive array of health notice types, each designed to monitor specific aspects of system operation and provide appropriate alerting for different categories of conditions. This comprehensive monitoring ensures that administrators are informed of all significant events that may require attention or intervention.
System Infrastructure Health Notices
Backend Error Notices are generated when the core rXg backend processes encounter error conditions that may impact system operation. These notices capture detailed information about the error context, affected processes, and potential impact on system functionality. Backend errors often indicate underlying system issues that require investigation and may signal the need for configuration changes or system maintenance.
Backend Warning Notices alert administrators to non-critical backend conditions that warrant attention but do not immediately threaten system operation. These may include queue configuration irregularities not caught by validation routines, minor process anomalies, or performance conditions approaching concerning levels. Backend warnings serve as early indicators of potential issues that may require proactive intervention.
Backend Failure Notices represent critical backend process failures that significantly impact system operation. These fatal-level notices indicate that core system functionality has been compromised and requires immediate administrative intervention to restore normal operation. Backend failures often require emergency response procedures and may necessitate system restart or failover operations.
CPU Core Temperature Notices monitor thermal conditions within the rXg hardware, alerting administrators when processor temperatures exceed safe operating thresholds. Elevated CPU temperatures can lead to system instability, performance degradation, and hardware damage if not addressed promptly. These notices help prevent thermal-related system failures and ensure reliable hardware operation.
Memory Utilization Notices track system memory usage and alert when available memory drops below configured thresholds. Memory exhaustion can lead to process failures, system instability, and service interruptions. These notices provide early warning of memory pressure conditions, allowing administrators to investigate memory usage patterns and take corrective action before critical conditions develop.
Disk Failure Notices detect hardware-level disk problems through system log analysis and direct hardware monitoring. These critical notices indicate potential or actual disk hardware failures that threaten data integrity and system availability. Disk failure notices require immediate attention to prevent data loss and may necessitate emergency backup and replacement procedures.
Filesystem Utilization Notices monitor disk space usage across all system filesystems and alert when available space drops below configured thresholds. Filesystem exhaustion can prevent normal system operation, block log writing, and interfere with user data storage. These notices help prevent disk space-related outages and provide guidance for capacity management.
Network Infrastructure Health Notices
Ping Target Monitor Notices track the reachability of operator-configured network targets through continuous ICMP ping testing. These notices help monitor network connectivity to critical infrastructure components, internet gateways, DNS servers, and other essential network services. Ping target failures can indicate network path problems, target system failures, or general connectivity issues that may impact user experience.
Uplink Monitor Notices specifically track the status of configured network uplinks by monitoring next-hop router reachability. Uplink failures can result in complete internet connectivity loss or force traffic onto backup connections. These critical notices require immediate attention to maintain network connectivity and service availability.
Access Point Monitor Notices track the connectivity and health status of managed wireless access points. These notices detect when access points become unreachable, experience configuration problems, or exhibit performance anomalies. Access point monitoring helps ensure wireless network reliability and coverage continuity.
IP Conflict Notices detect situations where multiple network devices attempt to use the same IP address, creating network communication problems and potential security issues. These notices help identify network configuration errors, DHCP misconfigurations, or unauthorized device activity that may disrupt network operations.
Interface Error Notices monitor network interface hardware for error conditions, performance problems, and connectivity issues. These notices help identify network hardware problems, cable faults, or configuration issues that may impact network performance and reliability.
Interrupt Storm Notices detect when network interfaces or other hardware components generate excessive interrupt activity that can impact system performance. Interrupt storms often indicate hardware problems, driver issues, or network conditions that require investigation and resolution.
Service-Specific Health Notices
DHCP Server Error Notices alert administrators when the DHCP service cannot start or encounters critical operational problems. DHCP service failures prevent new devices from obtaining network addresses and can disrupt existing network connectivity. These notices require immediate attention to restore network service functionality.
DHCP Pool Utilization Notices monitor IP address pool usage and alert when available addresses drop below configured thresholds. Address pool exhaustion prevents new devices from connecting to the network and can indicate the need for pool expansion or subnet reconfiguration.
DHCP Message Rate Notices detect potentially malicious DHCP request patterns that may indicate denial-of-service attacks or misconfigured network equipment. These notices help protect the DHCP service from abuse and maintain service availability during attack conditions.
Email Error Notices track problems with email notification delivery, including SMTP server connectivity issues, authentication failures, and message delivery problems. Email service problems can prevent administrators from receiving critical system notifications and may indicate broader network connectivity issues.
Portal Warning Notices detect problems with the captive portal system, including asset compilation failures, template processing errors, and service integration issues. Portal problems directly impact user experience and network access functionality.
Certificate Error Notices monitor SSL certificate validity and alert when certificates are approaching expiration or have become invalid. Certificate problems can prevent secure connections and may disrupt normal system operation if not addressed promptly.
PMS Connection Error Notices track connectivity to Property Management System integrations, alerting when communication failures occur. PMS integration problems can impact guest management, billing functionality, and automated system operations in hospitality environments.
License and Resource Limit Health Notices
Accounts Limit Notices monitor user account utilization against license restrictions, alerting when the number of configured accounts approaches licensed limits. Account limit notices help ensure compliance with licensing agreements and provide early warning of capacity constraints.
Login Sessions Limit Notices track active user sessions against license-defined limits, preventing license violations and ensuring system compliance. Session limit monitoring helps manage system resources and maintain licensing compliance.
States Limit Notices monitor packet filtering state table utilization, alerting when the number of active connection states approaches system limits. State table exhaustion can impact network performance and prevent new connections from being established.
Local IPs Limit Notices track the utilization of locally managed IP addresses against licensing restrictions, ensuring compliance with address management limits and preventing configuration errors that might violate licensing terms.
VLAN Utilization Notices monitor VLAN tag assignment pools in environments using per-user VLAN assignment, alerting when available VLAN tags become scarce. VLAN exhaustion can prevent new user authentication and may require pool expansion or configuration adjustment.
The comprehensive nature of the rXg health notice system ensures that administrators maintain complete visibility into all aspects of system operation, from low-level hardware conditions to high-level service delivery metrics. This extensive monitoring capability enables proactive system management, rapid problem identification, and informed decision-making for capacity planning and infrastructure optimization.
Through careful attention to health notice patterns and trends, administrators can identify emerging issues before they impact service delivery, plan capacity expansions based on actual utilization data, and maintain optimal system performance across all operational domains. The health notice system serves as both an operational monitoring tool and a strategic planning resource, providing the information necessary for effective infrastructure management and service delivery optimization.
Notification Events
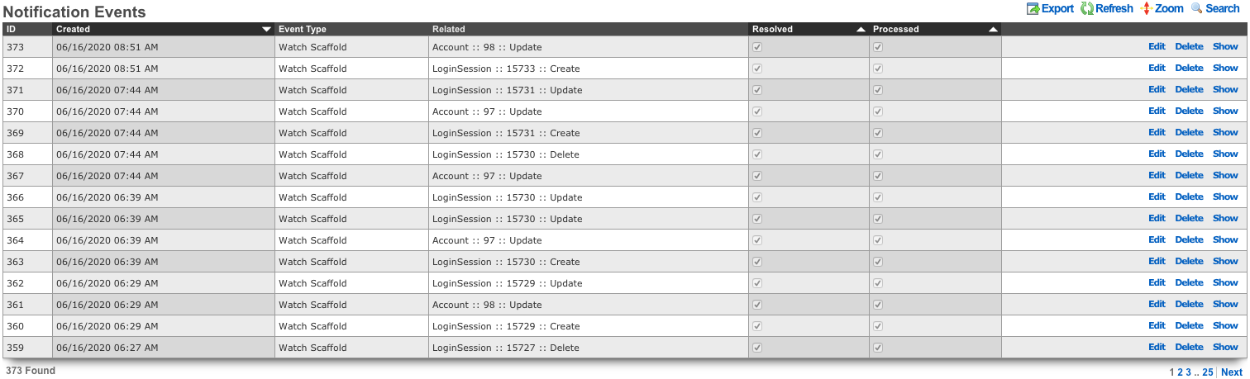
When a Notification Action is triggered a Notification Event will be logged by the rXg. It will list the ID of the event, the timestamp when it was Created , the Event Type , along with the Related object (Account, LoginSession, etc). The Resolved checkbox allows the operator to resolve any health notices generated from the event, editing the event and checking the resolved box will cure any health notices generated from the event. The Processed box indecates that the any responses to the event were completed.